When you think about national grid, it's easy to overlook just how crucial this infrastructure is to our daily lives. Powering homes, businesses, and industries, the national grid is the unsung hero of modern society. It’s like the nervous system of a country, ensuring that electricity flows seamlessly from power plants to your living room. But what exactly is the national grid, and why should you care? Let’s dive in and find out.
Imagine trying to live without electricity for even a day. Pretty rough, right? That’s where the national grid steps in. It’s not just some random wires strung across poles; it’s a sophisticated network that keeps everything running smoothly. From powering hospitals to charging your smartphone, the grid plays a vital role in almost everything we do.
But it’s not all about the big picture. Understanding the national grid can also help you make informed decisions about energy consumption, costs, and even sustainability. In a world where climate change is a growing concern, knowing how the grid operates and how it’s evolving can make a real difference.
Read also:Justin Fields Why I Chose Jets
What Exactly is the National Grid?
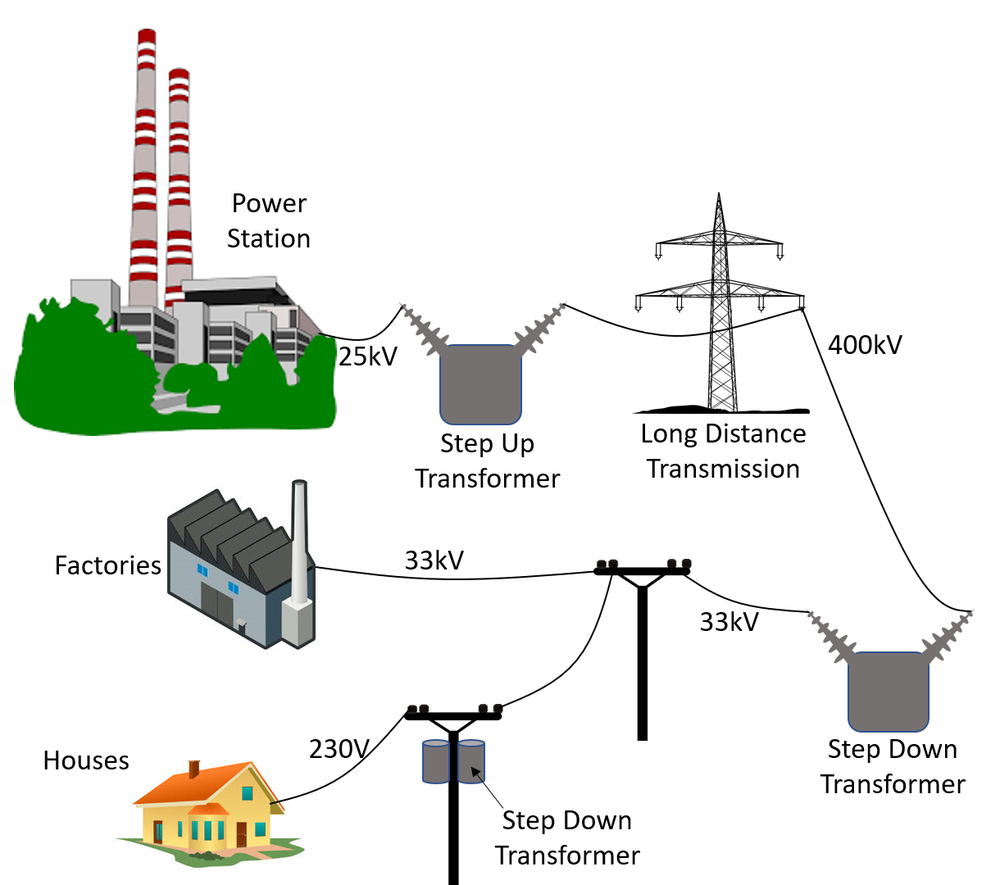
At its core, the national grid is a network of power lines, transformers, and substations that transmit electricity from generators to consumers. It’s like a highway system for electricity, designed to ensure that power is distributed efficiently and reliably. But it’s not just about moving electricity; it’s about balancing supply and demand in real-time.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Power Plants: These are where electricity is generated, using various sources like coal, natural gas, nuclear, wind, and solar.
- Transmission Lines: These high-voltage lines carry electricity over long distances to areas where it’s needed.
- Substations: These facilities reduce the voltage so it can be safely delivered to homes and businesses.
- Distribution Lines: These lower-voltage lines deliver electricity to individual consumers.
The national grid operates 24/7, ensuring that there’s always enough power to meet demand. It’s a complex system that requires constant monitoring and adjustments to keep everything running smoothly.
History of the National Grid
Believe it or not, the national grid hasn’t always been around. The concept of a centralized power distribution system evolved over time, driven by the need for more efficient and reliable electricity delivery. In the early days, power was generated locally, often using small generators that served specific areas.
But as cities grew and demand for electricity increased, the need for a more robust system became apparent. The first national grid systems were developed in the early 20th century, with countries like the UK and the US leading the way. Over the years, advancements in technology have allowed grids to become more efficient, resilient, and capable of integrating renewable energy sources.
Key Milestones in Grid Development
Here are some key moments in the history of the national grid:
Read also:Texas Senate Passes Bill To Ban Thc Products What You Need To Know
- 1930s: The Central Electricity Board in the UK establishes the first national grid system.
- 1950s: The U.S. expands its grid infrastructure to connect major cities and rural areas.
- 1970s: The introduction of computerized control systems improves grid efficiency.
- 2000s: The rise of renewable energy sources leads to new challenges and opportunities for grid operators.
How Does the National Grid Work?
Now that you know what the national grid is and where it came from, let’s take a closer look at how it actually works. The process starts at power plants, where electricity is generated using various methods. This electricity is then sent through transmission lines at high voltages to reduce energy loss over long distances.
Once it reaches a substation, the voltage is stepped down to a level that’s safe for distribution to homes and businesses. From there, it travels through distribution lines to individual consumers. The entire process is managed by grid operators who monitor supply and demand in real-time, making adjustments as needed to ensure stability.
The Role of Smart Grid Technology
In recent years, smart grid technology has revolutionized how the national grid operates. By incorporating sensors, data analytics, and automation, smart grids can improve efficiency, reduce outages, and better integrate renewable energy sources.
Here are some benefits of smart grid technology:
- Improved Reliability: Real-time monitoring allows for faster detection and response to issues.
- Increased Efficiency: Advanced analytics help optimize power distribution and reduce waste.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Smart grids make it easier to incorporate renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
Challenges Facing the National Grid
While the national grid is a marvel of modern engineering, it’s not without its challenges. One of the biggest issues is the need to balance supply and demand. As more people rely on electricity for everything from heating to transportation, the grid must adapt to meet growing demand.
Another challenge is the integration of renewable energy sources. While wind and solar power are great for the environment, they can be unpredictable, making it harder to maintain a stable supply. Additionally, aging infrastructure and cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to grid reliability.
Addressing Grid Challenges
So, how are these challenges being addressed? Here are a few strategies being implemented:
- Upgrading Infrastructure: Investing in new equipment and technology to improve efficiency and reliability.
- Expanding Renewable Energy: Building more wind and solar farms to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Enhancing Cybersecurity: Implementing advanced security measures to protect against cyber attacks.
The Future of the National Grid
As we look to the future, the national grid is poised for some exciting changes. One of the biggest trends is the increasing use of renewable energy sources. With advancements in battery storage and grid technology, it’s becoming easier to incorporate wind and solar power into the grid without compromising reliability.
Another trend is the rise of microgrids, which are small-scale grids that can operate independently of the main grid. These systems are ideal for remote areas or communities looking to reduce their reliance on traditional power sources.
Innovations in Grid Technology
Here are some innovations that could shape the future of the national grid:
- Advanced Battery Storage: Allowing for more efficient storage and distribution of renewable energy.
- Artificial Intelligence: Using AI to predict and respond to changes in supply and demand.
- Electric Vehicles: Integrating EV charging stations into the grid to support the growing number of electric cars.
The Impact of National Grid on Daily Life
It’s easy to take the national grid for granted, but its impact on daily life is immense. From powering hospitals and schools to keeping our homes comfortable, the grid touches almost every aspect of modern living. But it’s not just about convenience; the grid also plays a crucial role in economic development and environmental sustainability.
As countries work to reduce their carbon footprints, the national grid is becoming a key player in the transition to cleaner energy sources. By investing in renewable energy and smart grid technology, we can create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
Why Should You Care About the National Grid?
Here are a few reasons why understanding the national grid is important:
- Energy Independence: A reliable grid helps reduce dependence on foreign energy sources.
- Cost Savings: Efficient grid operation can lead to lower energy bills for consumers.
- Environmental Benefits: Integrating renewable energy sources helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the national grid is an essential part of modern life that often goes unnoticed. It’s the backbone of our energy infrastructure, ensuring that power is delivered reliably and efficiently to millions of people every day. Understanding how the grid works and the challenges it faces can help us make informed decisions about energy consumption and sustainability.
So, what can you do? Start by learning more about your local grid and how it’s evolving. Consider ways to reduce your energy consumption and support renewable energy initiatives. Together, we can help create a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. The more people understand the importance of the national grid, the better equipped we’ll be to tackle the challenges ahead.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is the National Grid?
- History of the National Grid
- How Does the National Grid Work?
- The Role of Smart Grid Technology
- Challenges Facing the National Grid
- Addressing Grid Challenges
- The Future of the National Grid
- Innovations in Grid Technology
- The Impact of National Grid on Daily Life
- Why Should You Care About the National Grid?